If you’ve ever witnessed someone suffer a stroke, you understand the humbling nature of this disease. It can reduce the mightiest human being to an immobile, helpless creature. Impairment of crucial functions like speech, walking, and control of bowel and bladder can wrench control from the body in a moment.
Even perpetually youthful TV personality Dick Clark was struck down by stroke at age 75, despite the outward appearance of perfect health. Clark’s stroke resulted in a six-week hospital stay and, judging from fragmented reports, significant disability. Stroke can be like a devastating fire that strikes without warning, leaving only smoldering rubble. Stroke can so ravage basic bodily functions that often all you can hope for is to regain a portion through rehabilitation.
The disease process that underlies stroke requires decades—30 or 40 years—to develop. With that much lead time, why aren’t we better able to detect or stop this crippling disease?
The truth is that we are able to predict many, if not most, strokes. Advances in imaging technology allow detection of atherosclerotic plaque that cause stroke years before it becomes a threat. Progress in deciphering the causes of stroke has also leapt forward.
Unfortunately, your neighborhood physician still focuses on diagnosing the crisis rather than anticipating it. Physicians prefer to deal with catastrophes and are just not that interested in prevention. Most physicians ask: “Is it time to operate or not?” The medical community obsesses over procedures like carotid endarterectomy (surgical removal of plaque) or carotid stents. Even when a person is afforded the warnings of a “mini-stroke”, or transient ischemic attack (TIA), little more is done once it’s determined that surgery is not necessary—even though this person has high risk for future stroke (50% over 10 years).
Let’s flip-flop this approach to stroke. Procedures represent a failure of prevention!
Where do strokes come from?
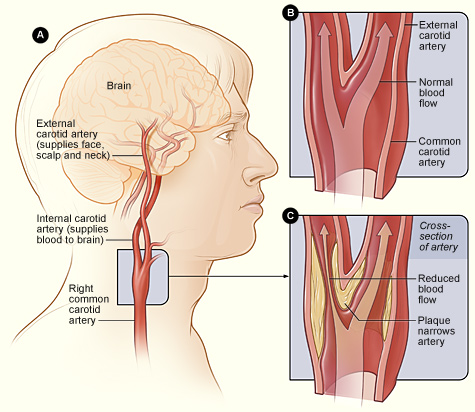
Stroke develops when some portion of the brain is deprived of blood. This usually results from a tiny bit of debris that dislodges from an atherosclerotic plaque along the walls of an artery (the same sort that accumulates in coronaries causing heart attack). The sources of debris have been a subject of controversy, but new imaging technologies have settled the question. Any blood vessel that leads from the heart to the brain can be a source. The two carotid arteries on both sides of your neck are a frequent source, as these arteries are prone to develop plaque. (Our discussion will be confined to what are called thromboembolic, or ischemic, strokes, i.e, strokes that occur from plaque that fragments, sending debris to the brain, and will not include the far less common hemorrhagic strokes due to rupture of small vessels in the brain, nor will we discuss atrial fibrillation and other heart causes of stroke. The thromboembolic strokes we discuss cause around 88% of all strokes.)
Over the last 10 years, the aorta has been recognized as another important source of stroke. The aorta is the main artery of the body whose branches go to the head, arms, and legs.
Atherosclerotic plaque is a live tissue that, through poor diet, inactivity, high cholesterol, overweight, etc., grows and becomes progressively more unstable. At some point, plaque fragments. Little bits break away, traveling to the brain. Fractured plaque also exposes its deeper structures to flowing blood, triggering blood clot formation, which in turn can also fragment and go to the brain. Atherosclerotic plaque is a prerequisite for the most common causes of stroke.
If the majority of strokes originate from plaque, why not measure plaque to determine if you’re at risk for stroke? How can we easily, safely, and accurately measure plaque in the carotid arteries and aorta? And if plaque can be measured, can it be shrunk or inactivated to reduce or eliminate risk for stroke?
How can plaque be measured?
Just 20 years ago, the only practical method of identifying plaque in the carotids or aorta was through angiography, requiring catheters inserted into the body to inject x-ray dye. Angiography was impractical as a screening measure.
CT scanning and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are emerging as exciting methods of imaging both carotids and aorta. Unfortunately, most centers and physicians are much more focused on the diagnostic uses of these technologies for people who have already suffered stroke or other catastrophe, and application of these devices for preventive uses is still evolving. One exception is when aortic calcification or aortic enlargement is incidentally noted on the increasingly popular CT heart scans; this is an important finding that can signal presence of aortic plaque.
The one test that is widely available and can be performed in just about any center is carotid ultrasound. It’s simple, painless, and precise. Two basic observations can be made:
1. Plaque detection—Atherosclerotic plaque can be clearly visualized. If plaque blocks more than 70% of the diameter of the vessel, or if there are “soft” (unstable) elements in plaque, then stroke risk may be high enough to justify surgery or stents. However, if there are plaques that are less severe, substantial risk for stroke may still be present that can be reduced with preventive measures.
2. Carotid intimal-medial thickness—This is a measure of the thickness of the lining of the carotid artery in areas not involved by plaque, but often precedes the development of mature plaque. Carotid intimal-medial thickness also provides an index of body-wide potential for atherosclerotic plaque that can place you at risk for stroke. The aorta, for instance, cannot be well imaged by surface ultrasound but can still be a source for stroke. Increased carotid intimal-medial thickness and carotid plaque are closely associated with likelihood of aortic plaque. The Rotterdam Study of 4000 participants demonstrated that if carotid intimal-medial thickness is greater than normal (1.0 mm), then you can be at risk for stroke (and heart attack), even if no carotid plaques are detected.
Carotid ultrasound is the one test you should consider that provides the most information with least effort. Ultrasound is harmless, painless, and can be obtained just about anywhere. Even if your doctor disagrees with your request for a carotid ultrasound, an increasing number of mobile services are popping up nationwide that make this test available for around $100. One important point: many scanners and interpreters will only report whether plaque is present or not. While this is important information, you should request that the carotid-intimal medial thickness be made as well. Not all centers can make this simple measure (because of software requirements), but it doesn’t hurt to try. Any amount of carotid plaque is reason to follow a preventive program, even if the plaque is insufficient to justify surgery.
Can plaque be reduced?
Can we shrink plaque in carotid arteries and aorta and thereby reduce, perhaps eliminate, these sources of stroke? That question is gaining momentum as effective therapies become available that pack real punch for reducing plaque.
Study after study has now documented that plaque can be reduced and, with it, risk for stroke. Reduction in plaque of 10–20% is possible within a year or two. Let’s consider the most potent influences on carotid and aortic plaque growth that need to be considered in a plaque-reducing program. (I assume that you are a non-smoker—if you are a smoker, you first need to concentrate on quitting.)
Hypertension
Considerable experience documents the power of blood pressure-lowering for prevention of stroke. The most recently updated guidelines, the JNC–VII, recommends a blood pressure of <140/90,>
Just how low should blood pressure be? The best evidence comes from the Camelot trial, conducted by the Cleveland Clinic’s Dr. Steve Nissen, in which 2000 participants with “normal” blood pressure of 129/78 were further reduced (with drugs amlodipine or lisinopril) to 125/75. This resulted in a 16% reduction in future heart attack and stroke in just two years. This bolsters the argument that the previously acceptable blood pressure of 140/90 may not protect you from stroke; further reduction may be in order.
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, and Hyperinsulinemia
Just being overweight increases risk of stroke. A Swedish study in 7400 obese men had double the risk of stroke compared to non-obese men. Increased body weight leads to diabetes and its close relations, metabolic syndrome and hyperinsulinemia (increased insulin levels), which play an overwhelmingly important role in increasing stroke risk. Of people who suffer strokes, a shocking 70% have one of these diagnoses. When diabetes is present, risk for stroke can be as much as six-fold higher.
Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance, predecessors of diabetes, are far more common than full-blown diabetes. Metabolic syndrome consists of excessive abdominal fat, high blood pressure, low HDL cholesterol, increased triglycerides, and resistance to insulin. Metabolic syndrome is rampant through the U.S, afflicting one of three adults due to sedentary lifestyles, processed foods, and overweight. High insulin levels and resistance to insulin are powerful drivers of plaque growth, and carotid plaque grows faster. Judging from the rapidly escalating prevalence of metabolic syndrome and diabetes in the population, it is likely that an epidemic of stroke is in our country’s future.
LipoproteinsSmall LDL, IDL, and Lipoprotein(a)
More than high cholesterol, various lipoprotein abnormalities carry greater risk for carotid and aortic plaque growth and stroke. Lipoproteins are fat-carrying proteins in blood that cause plaque growth. Patterns which are instigators of plaque growth and stroke include:
• Small LDL particlesSmall LDL particles cause carotid plaque growth more than large LDL particles. This abnormality also triples heart attack risk.
• Intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL)These triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (present even when triglycerides are low) are a measure of how effectively you clear fat from blood after a meal. IDL is a potent driver of carotid plaque growth. Increased IDL also creates fat-rich plaque that makes it more prone to fragment.
• Lipoprotein(a)This underappreciated lipoprotein is associated with heightened risk of stroke and heart attack by promoting blood clotting, constricting arteries, and increasing dangers of cholesterol. Carotid ultrasound studies have shown that lipoprotein(a) causes accelerated plaque growth.
Fibrinogen
This blood clotting protein not only causes carotid plaque growth, but also contributes to formation of unstable plaques, ones that have more inflammatory cells and a thinner tissue covering, making plaque more rupture-prone. An Oxford University analysis of 5000 participants confirmed the role of fibrinogen in increasing stroke risk. Fibrinogen levels >407 mg/dl heightens stroke risk six-fold.
C-reactive protein (CRP)
This measure of inflammation is proving to be a useful marker for identifying people at risk for stroke, with increased risk beginning at a level of 0.5 mg/l. High CRP also predicts more rapidly growing carotid plaque.
Homocysteine
Homocysteine is an important marker of increased likelihood of both carotid and aortic plaque, as well as stroke. In 1997, the European Concerted Action Project reported more than a doubling of stroke when homocysteine levels exceeded 12 mol/l. As homocysteine increases to 20 μmol/l, risk for stroke and heart attack increases an amazing 10-fold over that at a level of 9 μmol/l.
Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA)
ADMA is recently discovered amino acid whose blood levels can skyrocket up to 10-fold in the presence of hypertension, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, high cholesterol and triglycerides, obesity, and high homocysteine levels. ADMA blocks the action of the amino acid, l-arginine. This mimicry reduces the availability of nitric oxide, a powerful dilator and protector of arteries. ADMA levels in the top 10% predict a six-fold heightened risk for future stroke, and ADMA levels in people with strokes are double that in other people. A carotid ultrasound study in 116 subjects showed that higher blood levels of ADMA are associated with more severe carotid plaque. Because of ADMA’s shared role across a variety of abnormal conditions, correction or blocking the action of ADMA has been suggested as a unique therapeutic tool to reduce stroke risk.
Cholesterol
Data suggest that lowering cholesterol with statin cholesterol-lowering drugs slows carotid plaque growth and reduce stroke risk approximately 22%. An interesting study from the Cardiovascular Institute at Mt. Sinai School of Medicine in New York using the precise measuring ability of MRI of the carotids and thoracic aorta showed an impressive 20% regression of plaque area with simvastatin (Zocor®) taken for two years.
Although guidelines for cholesterol treatment recommend reduction of LDL cholesterol to 100 mg/dl in high-risk persons, a report from the Walter Reed Army Medical Center in Washington, DC, showed that carotid plaque was more effectively reduced when LDL cholesterol of 70 mg/dl or lower was achieved with statin cholesterol drugs. Lower LDL cholesterol may, therefore, be better.
Treatment Strategies to Reduce Carotid and Aortic Plaque
The essential question: How do we reduce carotid and aortic plaque? If we make this the focus of our efforts, many pieces begin to fall into place. If you’ve had any measure of carotid or aortic plaque such as a carotid ultrasound or aortic calcification on a CT heart scan, you know that you’re at increased risk for stroke. You also have a baseline for future comparison to gauge whether your program is working or not.
Because most people have not one but several causes of carotid and aortic plaque, there is no one single treatment that effectively eliminates risk for stroke. Instead, most people require a comprehensive program of healthy diet, exercise, supplements, and medication when indicated. Here, we focus on the nutritional supplements that can be critical components of your plaque-reduction program.
Fish oil
Fish oil is a cornerstone of your stroke prevention program. Epidemiological observations suggest a strong relationship of fish intake and reduction of stroke risk. Carotid ultrasound studies demonstrate less carotid plaque with greater intakes of fish.
A cleverly designed University of Southampton study made the fascinating observation that fish oil transforms the structure of carotid plaque. 150 people with severe carotid plaque scheduled for carotid endarterectomy (surgical removal of the plaque) were given fish oil, sunflower oil, or no treatment over several months while waiting for their procedure. (Delays in the British health system permitted this unique design.) Plaque was removed at surgery and examined. Participants taking fish oil had reduced inflammation in plaque and thicker tissue covering the fatty core, markers of more stable plaque. Those taking sunflower oil or no treatment had unstable plaques with greater inflammation and thinner, less sturdy covering tissue. This suggests that fish oil stabilizes carotid plaque, making it less likely to rupture and fragment.
A standard capsule of fish oil (containing 300 mg of EPA + DHA) contains the same amount of omega-3s as a 3 oz serving of cod or halibut; three capsules (900 mg DHA + EPA) contain the equivalent of a serving of farm-raised salmon. The dose that seems to provide greatest protection from stroke, lowers triglycerides (that form abnormal lipoproteins; see above), and reduces fibrinogen, is four capsules per day (1200 mg EPA + DHA).
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
Although there are no data specifically addressing whether CoQ10 reduces plaque, it is a marvelously effective way to reduce blood pressure, one of the crucial factors causing carotid and aortic plaque growth. A pooled analysis of eight studies showed that, on average, CoQ10 in daily doses of 50–200 mg reduced systolic blood pressure by 16 mm Hg, diastolic pressure by 10 mm Hg. Data suggest that CoQ10 can reverse abnormal heart muscle thickening (hypertrophy), another manifestation of high blood pressure, strongly suggesting that CoQ10 has benefits beyond just reducing pressure.
Supplements to correct the metabolic syndrome
Weight loss is, without question, the most immediate and direct path to correction of this dangerous pre-diabetic condition. A drop of even 10–20 lbs yields improvements across the board: increased sensitivity to insulin, increased HDL, and reductions in triglycerides, CRP, fibrinogen, small LDL particles, and blood pressure. Diet and exercise are fundamental components of an effort to lose weight; low carbohydrate or reduced glycemic index diets (e.g., South Beach or Mediterranean) rich in fibers are clearly effective. Several supplements can amplify weight-reduction efforts and be useful adjuncts to your lifestyle program. Among them:
White bean extract
White bean extract blocks intestinal absorption of carbohydrates by 66%. 1500 mg twice a day with meals yields, on average, 3–7 lbs of weight loss in the first month of use. The only side-effect is excessive gas, due to unabsorbed starches.
Glucomannan
This unique fiber taken prior to meals absorbs many times its weight in water and thereby fills your stomach. You consequently take in less food. Most people lose around four lbs per month using 1500 mg prior to each meal. Interestingly, glucomannan also blunts the rise in blood sugar after meals, an effect that, by itself, may lead to weight loss. Be sure to take with plenty of water.
DHEA
This adrenal hormone is key to maintaining physical stamina, mood, muscle mass in men, and libido in women. A recent randomized, placebo-controlled study at Washington University in 56 subjects showed a 13% decline in abdominal fat (fat that drives resistance to insulin) measured by MRI with 50 mg of DHEA per day at bedtime, along with improved sugar control and lower insulin levels.
Pectin, beta-glucan
Pectin is the soluble fiber in citrus rinds, green vegetables, and apples, also available as a supplement. Beta-glucan is the soluble fiber of oats and is also available as a supplement. Both are wonderful fibers that provide feelings of fullness, lower cholesterol, slow release of sugars, and can yield modest weight reduction. A USC study in 573 subjects using carotid ultrasound showed that greater intake of healthy fibers like pectin and beta-glucan is associated with less carotid plaque growth.
Folic acid, vitamins B6 and B12
Dr. Daniel Hackam at the Stroke Prevention and Atherosclerosis Research Centre in Ontario conducted a study using carotid ultrasound in 101 participants treated with folic acid 2.5 mg, vitamin B6 25 mg, and B12 250 mcg per day. Treatment resulted in plaque reduction, especially when homocysteine levels exceeded 14μmol/l at the start, compared to untreated participants who experienced substantial plaque growth.
An attempt to clarify the role of homocysteine treatment was made through a National Institute of Health-sponsored study of stroke prevention. 3680 participants with a prior history of stroke were enrolled and given either a “low-dose” (20 mcg folic acid, 0.2 mg B6, 6 mcg B12) or a “high-dose” (2.5 mg folic acid, 25 mg B6, 400 mcg B12) regimen. Although starting homocysteine levels showed a graded association with stroke risk (higher homocysteine levels predicted greater stroke risk), the treatment groups experienced, on average, only a 2 μmol drop in homocysteine levels and no reduction in stroke risk over two years. The study investigators as well as critics have suggested that the study failed due to an insufficient treatment period and that the doses were too low. (The doses we use in our plaque reduction program are folic acid 2.5–5.0 mg, B6 50–100 mg, B12 1000–2500 mcg.)
L-arginine
L-arginine can be used to overpower the adverse effects of ADMA. L-arginine is emerging as an important carotid plaque-reversing tool. Early reports in animals showed that l-arginine completely halted growth of aortic plaque, and did so more effectively than lovastatin (a cholesterol-lowering drug).
In humans, L-arginine reduces blood pressure, abnormal constriction of carotid and coronary arteries, blocks entry of inflammatory cells into plaque, increases sensitivity to insulin, and heightens exercise capacity. Following coronary angioplasty or stent placement, l-arginine results in up to 36% reduction in plaque growth.
The average American takes in 5400 mg of l-arginine through food every day. Supplementing with doses of 3000–12,000 mg per day has proven useful to correct many of these phenomena. (We use a dose of 6000 mg of l-arginine powder, twice a day on an empty stomach, dissolved in water, for our plaque regression program.) Does this result in a reduction of stroke risk? The emerging data suggest that l-arginine is likely to exert a powerful plaque-reducing and stroke-preventing benefit, but we await more clinical trial data.
Conclusion
Reducing stroke risk by reversing carotid and aortic plaque is becoming an everyday reality, with better tools becoming available. To know whether you’re at risk, the best and most available imaging tool is carotid ultrasound, aiming to identify intimal-medial thickness >1.0 mm, or carotid plaque. Any degree of calcification of the aorta, such as on a CT heart scan, is another useful measure of risk.
Treatment to reduce risk is multi-faceted but is based on examining all your sources of risk, including metabolic syndrome, small LDL, lipoprotein(a), and C-reactive protein. Fish oil is the one absolutely crucial ingredient in any stroke prevention program. Other supplements can be used in a targeted fashion, depending on the causes identified for your carotid or aortic plaque. Ideally, repeat scanning of your carotids should be done sometime after your program has begun to assess whether you’ve successfully achieved reversal of plaque growth.
 Stress in day to day living can build up to the point it creates anxiety attacks. These attacks can be very serious and can cause not only heart problems, but also stroke and low blood pressure.
Stress in day to day living can build up to the point it creates anxiety attacks. These attacks can be very serious and can cause not only heart problems, but also stroke and low blood pressure. So the heart is told to beat faster, but then, because the body needs to rest, the brain signals the heart to slow down. But the anxiety tells it to speed up. Everything is racing and everything is trying to slow down.
So the heart is told to beat faster, but then, because the body needs to rest, the brain signals the heart to slow down. But the anxiety tells it to speed up. Everything is racing and everything is trying to slow down.